Working with Triggers
Triggers execute Tabsdata functions. A trigger can be initiated manually through a CLI command or the UI, automatically by a new commit to its associated table, or through Crontab configurations.
Manual Triggers
Manual triggers are initiated by a CLI command or the UI.
For example, you can trigger a publisher to read sales data from a database table and publish it to the Tabsdata server.
You can manually trigger any Tabsdata function, even those with a specified automated trigger.
Using CLI
To trigger a function, use the following command in a command line interface:
$ td fn trigger --coll <collection_name> --name <function_name>
Where:
<collection_name>is the name of the collection in the Tabsdata server that the function is registered with.<function_name>is the name of the function to be executed. This name is defined when the function is registered.
Using UI
Click on the collection name “tutorial” on the left hand side or from the collection list to open the view containing further details regarding the collection.
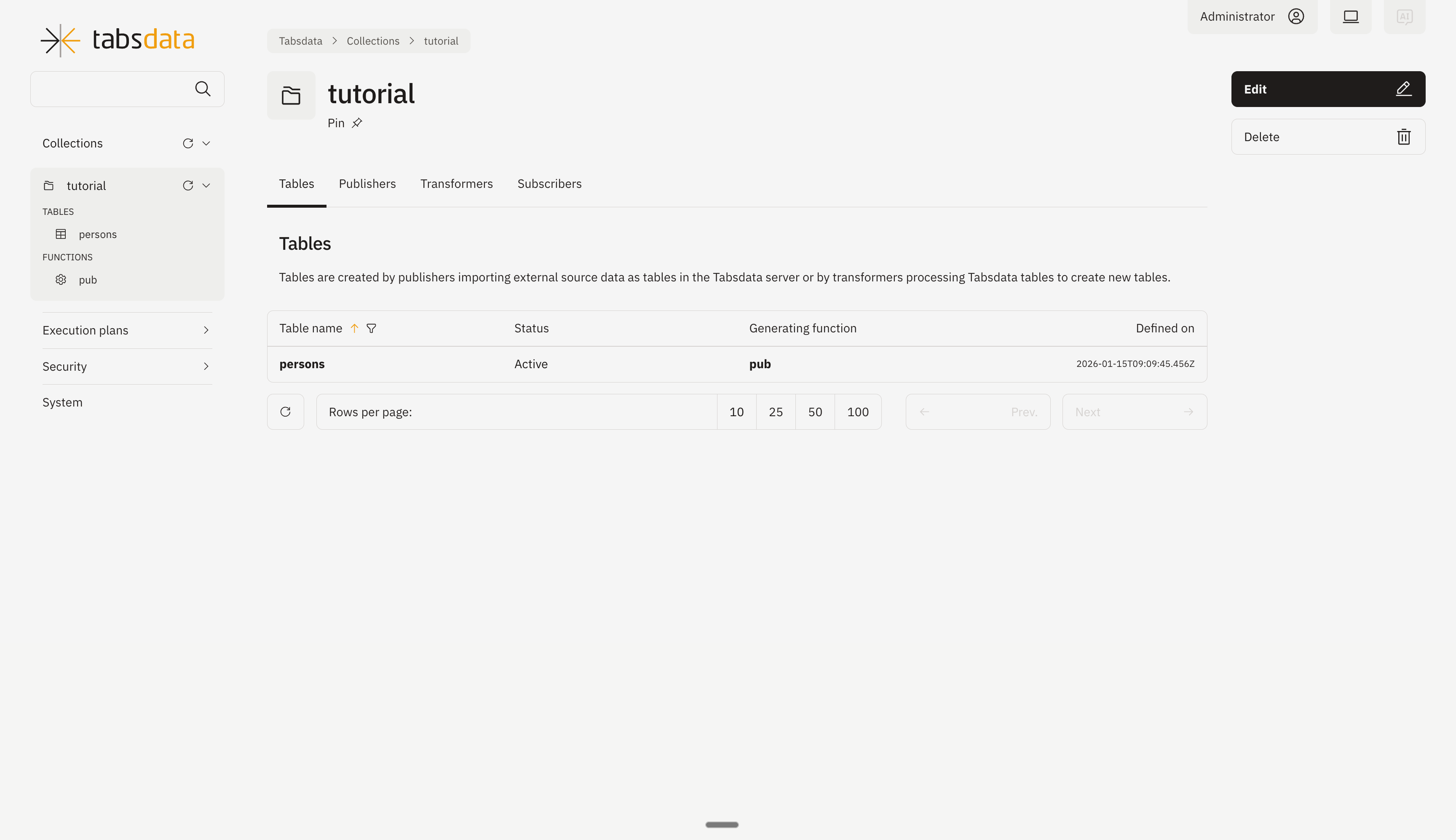
Click on “Publishers” to open the publishers registered in the collection.
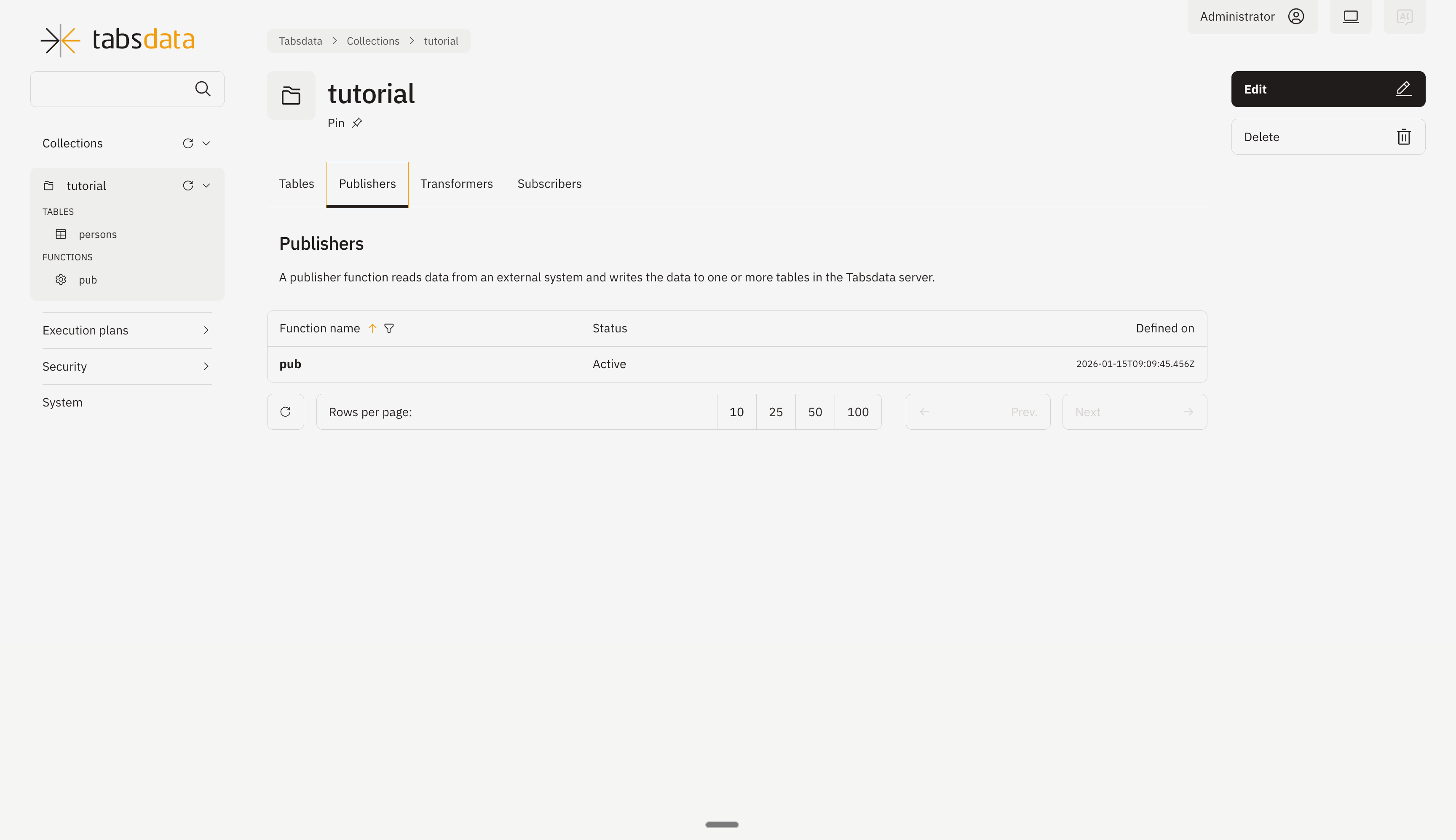
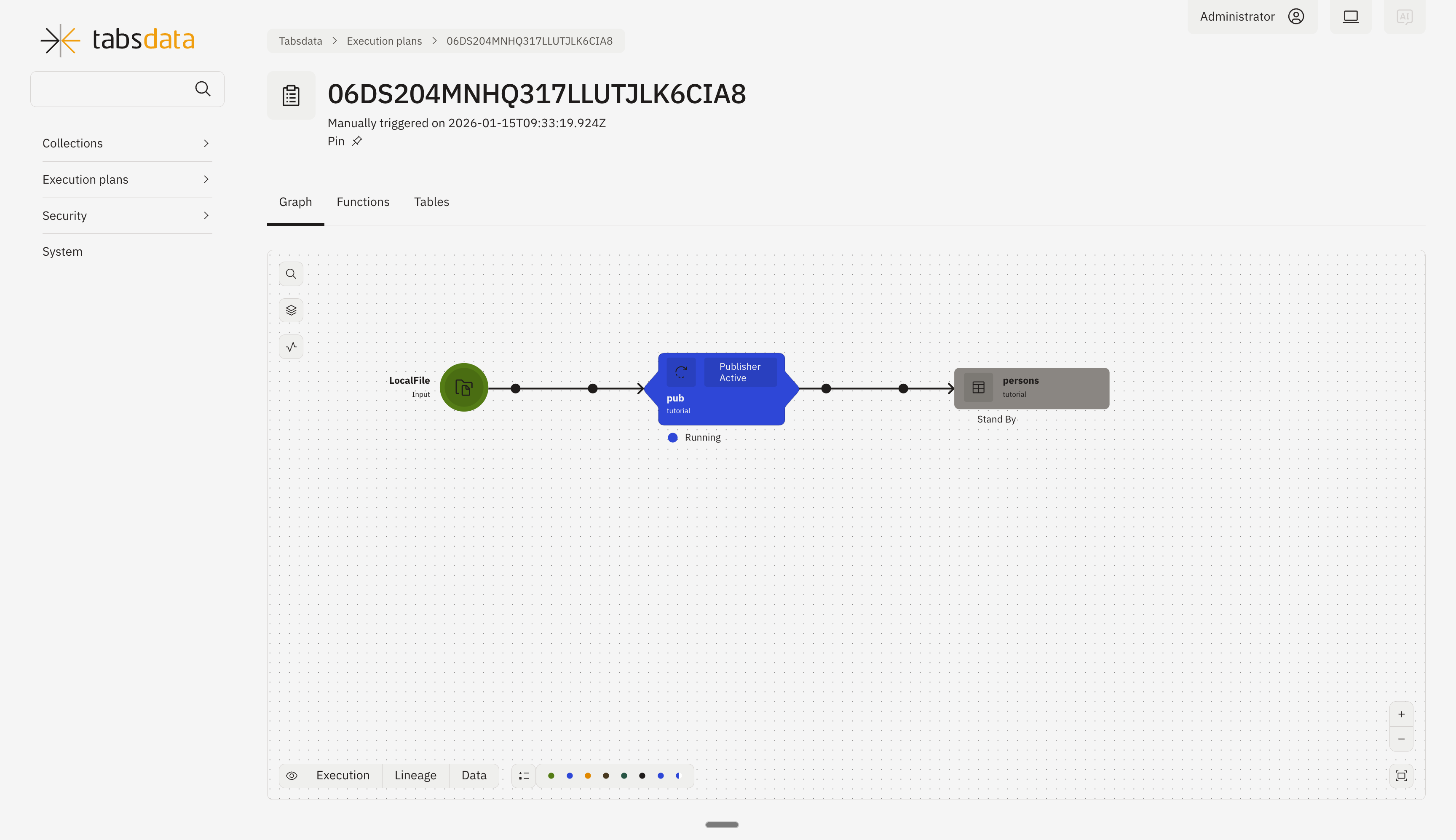
Open the publisher details by clicking on “pub” in the list. Click on trigger on the top right to trigger the execution of the publisher.
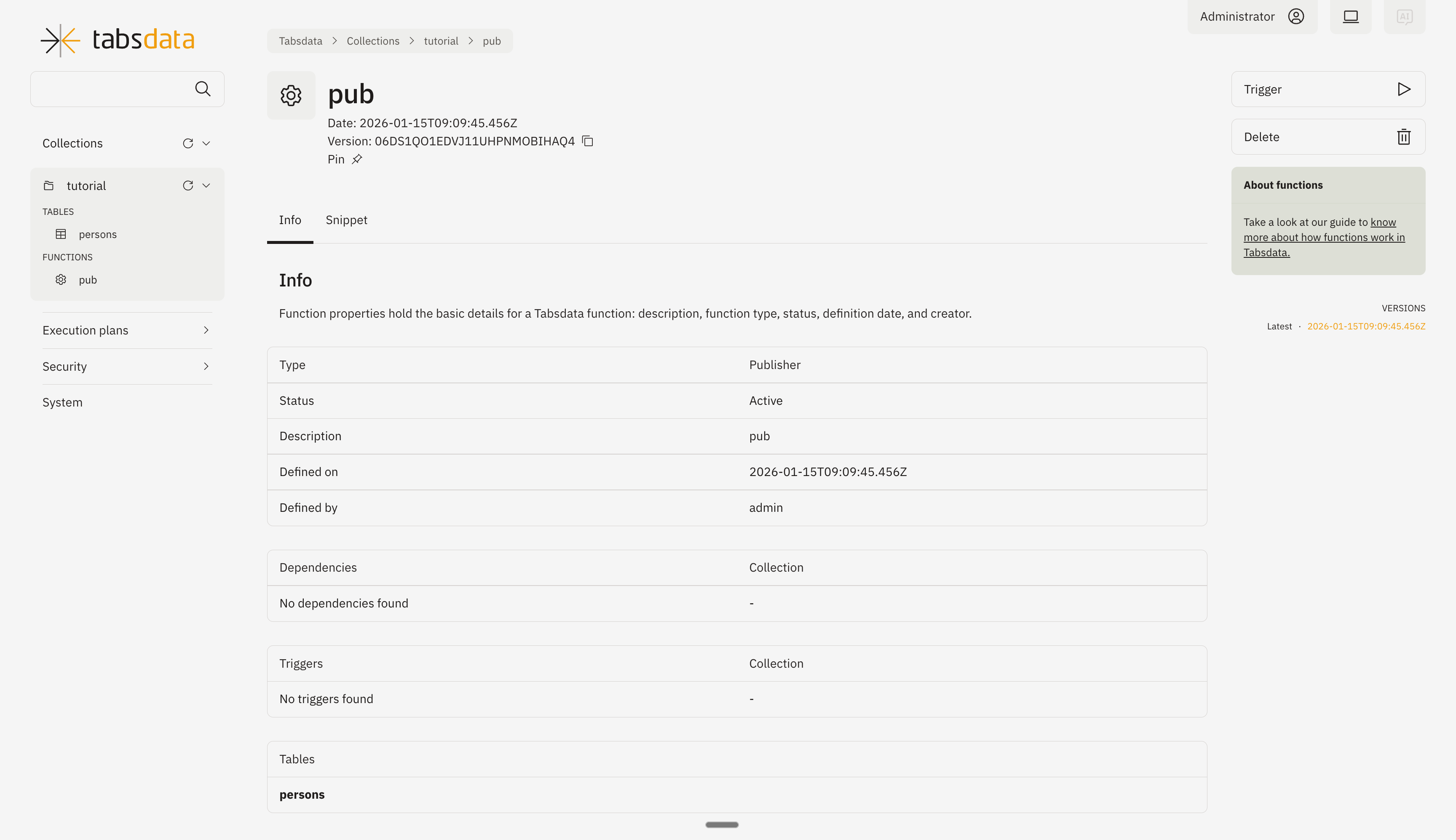
You can monitor the status of trigger through this diagram.
Automated Triggers
Automated triggers are initiated by a new commit to one of the tables associated with the function. For example, you might define an inventory subscriber function that exports data from a Tabsdata inventory table to AWS S3 every time the inventory table receives a commit.
Note that a commit does not always include changes in the table data. For example, a publisher that writes to three tables performs a commit to all three tables with each execution, irrespective of whether there is a change in data for any of the tables.
Since, the functions are automatically triggered which in turn create a new commit to other tables, Tabsdata enables a cascading workflow of updates to downstream tables.
trigger_by
Triggers in Tabsdata functions are defined using the trigger_by property.
Below are the different ways in which trigger_by can be configured:
Not Defining
If the trigger_by property is not defined, the behavior depends on the default behaviour of the function:
Publishers:
By default, publishers do not have any triggers. If trigger_by is not defined, the publisher can only be triggered manually.
Transformers:
By default, transformers are triggered by a commit to any of their input tables. Hence, if trigger_by is not defined, the transformer will automatically respond to new commits to any of its input tables. To specify different trigger tables, define the trigger_by tables using a non-empty array.
Subscribers:
By default, subscribers are triggered by a commit to any of its input tables. Hence, if trigger_by is not defined, the subscriber will automatically respond to new commits to any of its input tables. To specify different trigger tables, define the trigger_by tables using a non-empty array.
Defining an Empty Array
trigger_by = []
Setting trigger_by to an empty array disables automatic triggering. This is useful for transformers and subscribers when you want to prevent them from being triggered by their input tables.
Defining a Non-Empty Array
trigger_by = ["<table_name>", "<collection_name>/<table_name>"]
Setting trigger_by to a non-empty array explicitly defines which tables can trigger the function. If you want the functions to be triggered by a subset of their input tables or by external tables, list them in the array. To reference tables outside the function’s collection, use the format <collection_name>/<table_name>.
Only those tables listed in the trigger_by array will trigger the function. List as many as needed.
Crontab Triggers
With Crontab triggers, Publishers, Subscribers, and Transformers can be configured to run periodically within Tabsdata without the need for manual triggers or external schedulers.
Similar to automated triggers, you work with the trigger_by parameter. However, unlike automated triggers, the trigger_by parameter must be configured with a `CronTrigger` object.
The CronTrigger object requires a Unix crontab mask and accepts optional start and end parameters.
Note: Tabsdata uses the UTC timezone to interpret all crontab schedules.
Configuration Parameters
The mask Parameter
The mask parameter defines the frequency of the execution. It follows the standard Unix crontab specification consisting of 5 elements with minute precision.
Syntax: Minute Hour Day Month Day-of-Week
Extensions: Non-standard extensions (e.g., @hourly, @daily) are not supported.
Examples
Mask |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Runs every 30 minutes (at the top of the hour and at minute 30). |
|
Runs daily at the beginning of the day (00:00 UTC). |
|
Runs at 10:00 PM (22:00 UTC) every Friday. |
References
The start and end Parameters
These optional parameters define a specific window of time during which the schedule is valid.
- Format:
A Python datetime object with timezone information.
An ISO 8601 string in the UTC timezone (e.g., 2024-01-01T12:00:00Z).
- Behavior:
If specified: Tabsdata will only trigger the function based on the mask between the start and end times.
If omitted: Tabsdata will trigger the function indefinitely based on the mask, starting from the moment the function is successfully registered.
Trigger Scheduling Lifecycle
The execution of Crontab triggers is dependent on the enabled status of the function.
Registration: When registering or updating a function, it can be set as enabled (default) or disabled via the td command line interface.
- Runtime Control: An existing function can be toggled between enabled and disabled states using the td command line.
Enabled: Tabsdata will trigger the function according to the defined crontab mask.
Disabled: Tabsdata will ignore the crontab mask and the function will not trigger automatically.
Example
The following is an example of a Publisher configured to trigger at the beginning of every hour.
@td.publisher(
trigger_by=CronTrigger("0 * * * *"),
source=td.MySQLSource(
uri="mysql://my-host:3306/my-db",
query="SELECT * FROM my_table",
credentials=td.UserPasswordCredentials("root", "mysql"),
),
tables="my_table"
)
def my_publisher(t: tdf.TableFrame) -> tdf.TableFrame:
return t